MySQL5.7 lossless 半同步复制
1. 简介
MySQL5.7版本的半同步复制(semi-synchronous ),解决了在主机或者网络在数据同步阶段出现问题时数据不一致的问题,所以官方称其为lossless replication。
在半同步复制过程中,使用普通方式(after commit)还是无损复制(after sync),使用rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_point进行配置,该参数有两种值,本文将进行介绍。
2. AFTER SYNC & AFTER COMMIT
& 在官方文档中,有如下两种数据同步的方式:
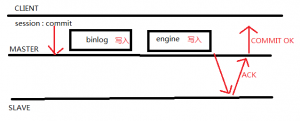
AFTER_SYNC (the default): The master writes each transaction to its binary log and the slave, and syncs the binary log to disk. The master waits for slave acknowledgment of transaction receipt after the sync. Upon receiving acknowledgment, the master commits the transaction to the storage engine and returns a result to the client, which then can proceed.
主库把每一个事务写到二进制日志并保存磁盘上,且发送给从库。主库在等待从库写到自己的relay-log里确认信息。在接到确认信息后,主数据库把事务写到存储引擎里并把相应结果反馈给客户端,客户端将在那时进行处理。
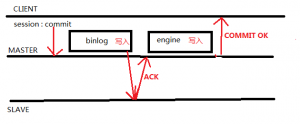
AFTER_COMMIT: The master writes each transaction to its binary log and the slave, syncs the binary log, and commits the transaction to the storage engine. The master waits for slave acknowledgment of transaction receipt after the commit. Upon receiving acknowledgment, the master returns a result to the client, which then can proceed.
主库把每一个事务写到二进制日志并保存磁盘上,且发送给从库,并把事务写到存储引擎里。主库在等待从库写到自己的relay-log里确认信息。在接到确认信息后,主库把相应结果反馈给客户端,客户端将在那时进行处理。
3. 两种数据commit方式的差异:
• With AFTER_SYNC, all clients see the committed transaction at the same time: After it has been acknowledged by the slave and committed to the storage engine on the master. Thus, all clients see the same data on the master.
In the event of master failure, all transactions committed on the master have been replicated to the slave (saved to its relay log). A crash of the master and failover to the slave is lossless because the slave is up to date. Note, however, that the master cannot be restarted in this scenario and must be discarded, because its binary log might contain uncommitted transactions that would cause a conflict with the slave when externalized after binary log recovery.
AFTER_SYNC: 当master宕机时,所有在maser上已经提交的事务已经被复制到slave上(slave的relay log中)。所以master的宕机对于从库来说,是不会丢失数据的,因为slave已经有了最新的数据。注意:若master宕机,不能将主机重新进入集群,必须将其从集群中“踢出”,因为master的binary log可能已经包含了未提交的事务(uncommitted transactions),当master重启进行binary log recovery时,会导致这部分事务和slave的已提交的事务冲突。
• With AFTER_COMMIT, the client issuing the transaction gets a return status only after the server commits to the storage engine and receives slave acknowledgment. After the commit and before slave acknowledgment, other clients can see the committed transaction before the committing client.
If something goes wrong such that the slave does not process the transaction, then in the event of a master crash and failover to the slave, it is possible that such clients will see a loss of data relative to what they saw on the master.
AFTER_COMMIT: 当slave没有收到master发送的数据(binlog)时,此时master宕机,在slave上将不能看到在master上已经提交的这部分事务的数据。
4. 两种方式性能对比
两种方式的commit路径:

在半同步复制中,若出现复制线程卡主,可以看到“Waiting for semi-sync ACK from slave” 的状态。那此时两种路径,等待的阶段则不同:
- 对于after sync(即lossless),事务阻塞在等待slave将binary log写入relay log并flush disk的ACK,此时事务没有commit;
- 对于after commit(即普通的semi-sync),事务commit后,等待slave将binary log写入relay log并flush disk的ACK。
**由此可推断:after sync的性能优于after commit: **
因为after sync在等到从库写relay log时,可以堆积事务,在下一个commit阶段进行group commit。
5. rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout配置
对于数据的一致性,可通过rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout进行配置:
变量解释:
A value in milliseconds that controls how long the master waits on a commit for acknowledgment from a slave before timing out and reverting to asynchronous replication
即当semi-synchronous等待超时时,转为异步同步的超时时间。
根据CAP理论:
- 【C】 一致性
- 【A】 可用性
- 【P】 分区容忍性
三者不可兼得,至少需牺牲其中一个
- 若将rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout设置为很大,即牺牲可用性,则可以得到数据的强一致性;
- 若将rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout设置为很小或直接使用原生的异步复制,即牺牲强一致性,能获取到更快的速读(可用性)。
在实际生产环境中需要进行权衡,配置合适的值。
