MySQL源码-Seconds_Behind_Master的计算
一、目的
Replication作为MySQL的通用高可用方案的基础,常常需要观察主从延迟,我们通常监测show slave status中的“Seconds_Behind_Master”指标,获取主从延迟的时间,该参数具体是什么含义呢?
-
在业务中,若主库的写入较大,则可能会导致Seconds_Behind_Master的值很大;
-
也有可能Seconds_Behind_Master=0,但是主从已经出现了较大的延迟。
所以本文则一探究竟,看看这个值是怎么计算得到的。
二、查看源码
1、查找文件位置
通常我习惯过滤以下类型文件:
1
*.result,*.inc,*.test,*.opt,*.cnf,*.txt
2、查看计算公式
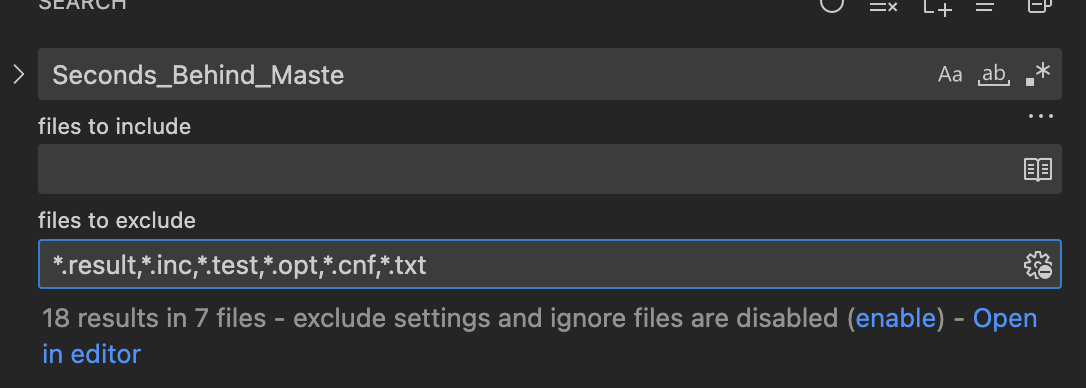
在sql->rpl_replica.cc文件中有如下的注释,为伪代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/*
The pseudo code to compute Seconds_Behind_Master:
if (SQL thread is running)
{
if (SQL thread processed all the available relay log)
{
if (IO thread is running)
print 0;
else
print NULL;
}
else
compute Seconds_Behind_Master;
}
else
print NULL;
*/
 即:
即:
- 若SQL线程是not running的状态,则返回NULL
- 若SQL线程running + 已经处理完所有的relay log + IO线程running,则返回0;
- 若SQL线程running + 已经处理完所有的relay log + IO线程not running,则返回NULL;
- 若SQL线程running + 未处理完所有的relay log,则计算Seconds_Behind_Master;
判断是否处理完所有的relay log:
1
2
3
4
Check if SQL thread is at the end of relay log
Checking should be done using two conditions
condition1: compare the log positions and
condition2: compare the file names (to handle rotation case)
对比日志log positions和file names。
真实计算代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
if (mi->rli->slave_running) {
if ((mi->get_master_log_pos() == mi->rli->get_group_master_log_pos()) &&
(!strcmp(mi->get_master_log_name(),
mi->rli->get_group_master_log_name()))) {
if (mi->slave_running == MYSQL_SLAVE_RUN_CONNECT)
protocol->store(0LL);
else
protocol->store_null();
} else {
long time_diff = ((long)(time(nullptr) - mi->rli->last_master_timestamp) - mi->clock_diff_with_master);
protocol->store(
(longlong)(mi->rli->last_master_timestamp ? max(0L, time_diff) : 0));
}
} else {
protocol->store_null();
}
protocol->store(mi->ssl_verify_server_cert ? "Yes" : "No", &my_charset_bin);
即总体公式为:
- long time_diff = ((long)(time(nullptr) - mi->rli->last_master_timestamp) - mi->clock_diff_with_master);
3、公式中的变量值
(1) 获取clock_diff_with_master:
1
2
3
4
5
6
The difference in seconds between the clock of the master and the clock of the slave (second - first). It must be signed as it may be <0 or >0.
clock_diff_with_master is computed when the I/O thread starts; for this the I/O thread does a SELECT UNIX_TIMESTAMP() on the master.
"how late the slave is compared to the master" is computed like this:
clock_of_slave - last_timestamp_executed_by_SQL_thread - clock_diff_with_master
在I/O线程启动时,会在master上执行SELECT UNIX_TIMESTAMP(),得到主库的时间戳。
(2) last_master_timestamp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
ptr_ev = &ev;
/*
Even if we don't execute this event, we keep the master timestamp, so that seconds behind master shows correct delta (there are events that are not replayed, so we keep falling behind).
If it is an artificial event, or a relay log event (IO thread generated event) or ev->when is set to 0, or a FD from master, or a heartbeat event with server_id '0' then we don't update the last_master_timestamp.
In case of parallel execution last_master_timestamp is only updated when a job is taken out of GAQ. Thus when last_master_timestamp is 0 (which indicates that GAQ is empty, all slave workers are waiting for events from the Coordinator), we need to initialize it with a timestamp from the first event to be executed in parallel.
*/
if ((!rli->is_parallel_exec() || rli->last_master_timestamp == 0) &&
!(ev->is_artificial_event() || ev->is_relay_log_event() ||
ev->get_type_code() == binary_log::FORMAT_DESCRIPTION_EVENT ||
ev->server_id == 0)) {
rli->last_master_timestamp = ev->common_header->when.tv_sec + (time_t)ev->exec_time;
assert(rli->last_master_timestamp >= 0);
}
-
last_master_timestamp = master上event开始时间 + 执行耗时
-
对于并行复制: last_master_timestamp仅在GAQ序列消费完毕时更新,若GAQ为空,last_master_timestamp更新为0 ( In case of parallel execution last_master_timestamp is only updated when a job is taken out of GAQ. If GAQ is empty, set it to zero.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
/*
We need to ensure that this is never called at this point when cnt is zero. This value means that the checkpoint information will be completely reset.
*/
/*
Update the rli->last_master_timestamp for reporting correct Seconds_behind_master.
If GAQ is empty, set it to zero.
Else, update it with the timestamp of the first job of the Slave_job_queue which was assigned in the Log_event::get_slave_worker() function.
*/
ts = rli->gaq->empty()
? 0
: reinterpret_cast<Slave_job_group *>(rli->gaq->head_queue())->ts;
rli->reset_notified_checkpoint(cnt, ts, true);
/* end-of "Coordinator::commit_positions" */
GAQ的含义:
1
2
3
/*
master-binlog ordered queue of Slave_job_group descriptors of groups that are under processing. The queue size is @c checkpoint_group.
*/
(3) 状态更新间隔
-
更新间隔,在8.0中,新增参数: slave_checkpoint_period:毫秒
-
更新间隔,在5.7: the checkpoint routine is being called by the SQL Thread 参考:rpl_slave
(4) 部分异常状态值的说明
sql->rpl_replica.cc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/*
Apparently on some systems time_diff can be <0. Here are possible reasons related to MySQL:
- the master is itself a slave of another master whose time is ahead.
- somebody used an explicit SET TIMESTAMP on the master.
Possible reason related to granularity-to-second of time functions (nothing to do with MySQL), which can explain a value of -1:
assume the master's and slave's time are perfectly synchronized, and that at slave's connection time, when the master's timestamp is read, it is at the very end of second 1, and (a very short time later) when the slave's timestamp is read it is at the very beginning of second 2.
Then the recorded value for master is 1 and the recorded value for slave is 2. At SHOW REPLICA STATUS time, assume that the difference between timestamp of slave and rli->last_master_timestamp is 0
(i.e. they are in the same second),
then we get 0-(2-1)=-1 as a result. This confuses users, so we don't go below 0: hence the max().
last_master_timestamp == 0 (an "impossible" timestamp 1970) is a special marker to say "consider we have caught up".
*/
- time_diff可能会小于0:
- master本身作为另一个master的slave,并且另一个msater的时间更向前。
- time_diff = -1的情况: 假设master和slave的时间完全同步,I/O线程读取master的时间戳的时候在1秒最后,slave的时间戳在2秒开头:0-(2-1)=-1
所以最终,long time_diff = ((long)(time(nullptr) - mi->rli->last_master_timestamp) - mi->clock_diff_with_master);为Seconds_Behind_Master的计算。
